GCSE Physics - Revision
Level
|
Board
|
Subject
|
Paper
|
Assessment Type
|
Length
|
% of Course
|
|
GCSE
|
AQA
|
Physics
|
Paper 1: Energy; Electricity; Particle model of matter; and Atomic structure
|
Written Exam
|
1h 45m
|
50%
|
|
Paper 2: Forces; Waves; Magnetism and electromagnetism; and Space physics
|
Written Exam
|
1h 45m
|
50%
|
Revision strategies
Where do I Start?
There is a lot to learn in Science, especially when you are taking Biology, Chemistry and Physics as separate GCSEs. That is why you need to start your revision early and organise your time. The first step is to get your hands on the syllabus for each subject. All the Science course specifications are extremely useful, because they provide clear definitions for terms you must be familiar with and tell you which examples, processes and practicals you need to remember in detail.
Go through the syllabus to work out the bits you are most and least confident on. If you are unfamiliar with any subject content, look it up in revision guides or using the internet
You can find your Physics specification here.
Specific revision strategies
- Make spider diagrams / mind maps
- Make notes – but not too many. Don’t just copy out text, read a paragraph and summarise it.
- Use flashcards/formula cards.
- Use diagrams, flow charts, equations and formula triangles to help you visualise ideas in different ways.
- Review key terms, and definitions to ensure you are confident with these as you will need to use the correct language in the exams.
- Regularly review ideas and test yourself on these
- Ensure you learn and can use the physics equations you will need for your exams.
- Don’t forget to revise the required practicals as these will also be in your exams. Make sure you are confident in the methods, and skills used practical work including drawing graphs, analysing data, interpreting variables, drawing conclusions and evaluating.
Revision areas
Paper 1
Unit 1: Energy
- Energy stores and systems
- Changes in energy
- Energy changes in systems
- Power
- Energy transfers in a system
- Efficiency
- National and global energy resources
Unit 2: Electricity
- Standard circuit diagram symbols
- Electrical charge and current
- Current, resistance and potential difference
- Resistors
- Series and parallel circuits
- Direct and alternating potential difference
- Mains electricity
- Power
- Energy transfers in everyday appliances
- The National Grid
- Static charge
- Electric fields
Unit 3: Particle model of matter
- Density of materials
- Changes of state
- Internal energy
- Temperature changes in a system and specific heat capacity
- Changes of heat and specific latent heat
- Particle motion in gases
- Pressure in gases
- Increasing the pressure of a gas
Unit 4: Atomic structure
- The structure of an atom
- Mass number, atomic number and isotopes
- The development of the model of the atom
- Radioactive decay and nuclear radiation
- Nuclear equations
- Half-lives and the random nature of radioactive decay
- Radioactive contamination
- Background radiation
- Different half-lives of radioactive isotopes
- Uses of nuclear radiation
- Nuclear fission
- Nuclear fusion
Required practical activities
- Required practical activity 1: Investigation to determine the specific heat capacity of materials.
- Required practical activity 2: Investigate the effectiveness of different materials as thermal insulators and the factors that may affect the thermal insulation properties of a material.
- Required practical activity 3: Use circuit diagrams to set up and check appropriate circuits to investigate the factors affecting the resistance of electrical circuits.
- Required practical activity 4: Use circuit diagrams to construct appropriate circuits to investigate the I–V characteristics of a variety of circuit elements.
- Required practical activity 5: Use appropriate apparatus to make and record the measurements needed to determine the densities of regular and irregular solid objects and liquids.
Paper 2
Unit 5: Forces
- Scalar and vector quantities
- Contact and non-contact forces
- Gravity
- Resultant forces
- Work done and energy transfer
- Forces and elasticity
- Moments, levers and gears
- Pressure in a fluid
- Atmospheric pressure
- Describing motion along a line
- Speed
- Velocity
- The distance–time relationship
- Acceleration
- Forces, accelerations and Newton's Laws of motion
- Stopping distance
- Reaction time
- Factors affecting braking distance
- Momentum (HT only)
- Changes in momentum
Unit 6: Waves
- Transverse and longitudinal waves
- Properties of waves
- Reflection of waves
- Sound waves
- Waves for detection and exploration
- Types of electromagnetic waves
- Properties of electromagnetic waves
- Uses and applications of electromagnetic waves
- Lenses
- Visible light
- Black body radiation
- Perfect black bodies and radiation
Unit 7: Magnetism and electromagnetism
- Poles of a magnet
- Magnetic fields
- Electromagnetism
- Fleming's left-hand rule (HT only)
- Electric motors (HT only)
- Loudspeakers
- Induced potential
- Uses of the generator effect
- Microphones
- Transformers
Unit 8: Space physics
- Our solar system
- The life cycle of a star
- Orbital motion, natural and artificial satellites
- Red-shift
Required practical activities
- Required practical activity 6: Investigate the relationship between force and extension for a spring.
- Required practical activity 7: Investigate the effect of varying the force on the acceleration of an object of constant mass, and the effect of varying the mass of an object on the acceleration produced by a constant force.
- Required practical activity 8: To measure the frequency, wavelength and speed of waves in a ripple tank and waves in a solid.
- Required practical activity 9 Investigate the reflection of light by different types of surface and the refraction of light by different substances.
- Required practical activity 10: Investigate how the amount of infrared radiation absorbed or radiated by a surface depends on the nature of that surface.
Physics equations students are required to learn
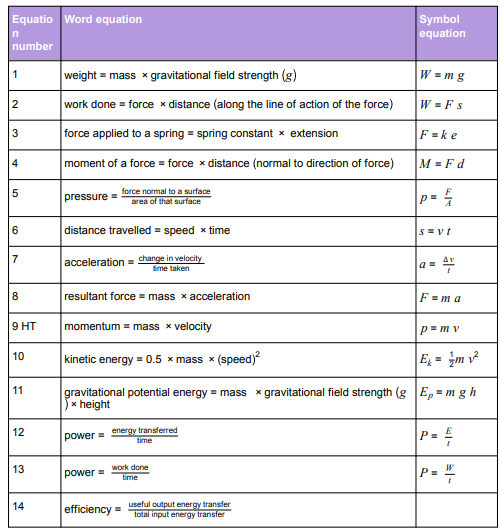
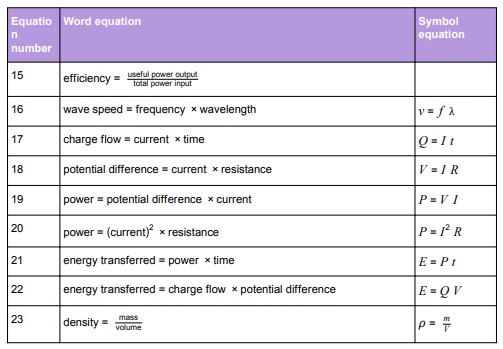
Physics equations students will be given in the exam
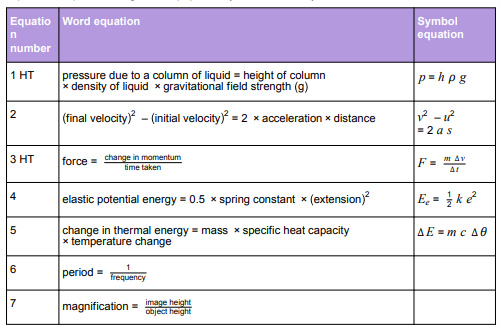
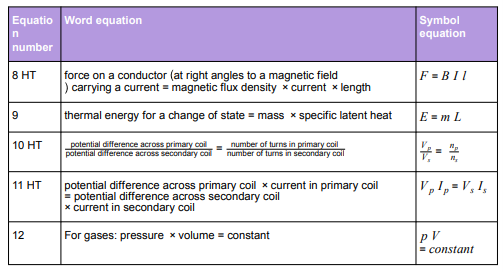
Websites
Past papers
It is vital you do past papers and mark them yourself. Exam practice is important as the examiner will want to see you can apply the scientific ideas you have been studying, and past papers will show how this is done. Follow this link to access Physics past papers.



